Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19: Accuracy and Considerations
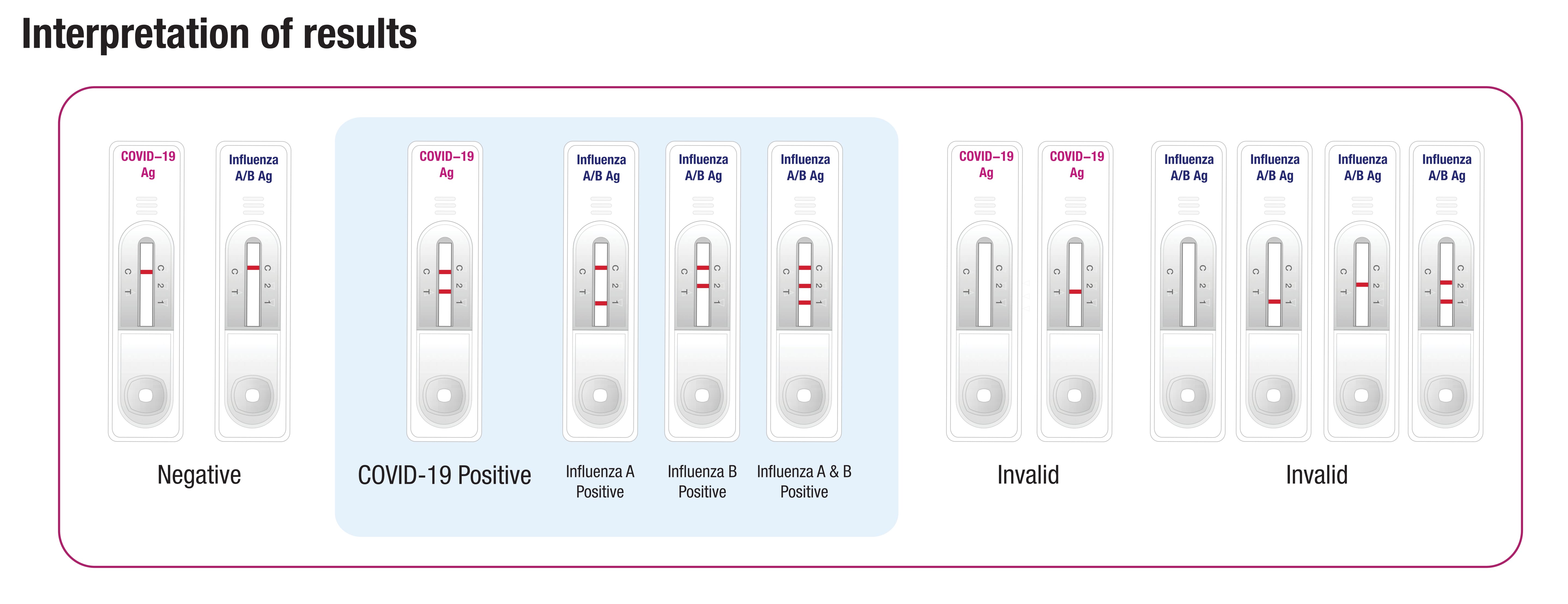
Sensitivity and Specificity
Rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 are generally less sensitive than molecular tests, such as PCR tests, in detecting the virus. Sensitivity refers to the ability of a test to correctly identify individuals who have the disease. Antigen tests may be less likely to detect the virus in people with low levels of the virus, such as those who are early in the course of the infection or those who have been vaccinated.
The specificity of rapid antigen tests, which refers to the ability of a test to correctly identify individuals who do not have the disease, is generally high. This means that rapid antigen tests are good at ruling out COVID-19 infection in people who do not have symptoms or who have been exposed to someone with COVID-19 but do not have the infection themselves.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
The accuracy of rapid antigen tests can be affected by several factors, including:
- Timing of the test: Rapid antigen tests are most accurate when performed within the first few days of symptom onset.
- Type of sample: Nasal swabs are generally more accurate than saliva or throat swabs.
- Quality of the test: The accuracy of rapid antigen tests can vary depending on the brand and manufacturer of the test.
- User error: Incorrectly performing the test can affect the accuracy of the results.
When to Use Rapid Antigen Tests
Rapid antigen tests are most useful for:
- Screening people with symptoms of COVID-19: Rapid antigen tests can help to quickly identify people who are likely to have COVID-19 and need to isolate to prevent spreading the virus to others.
- Testing people who have been exposed to someone with COVID-19: Rapid antigen tests can help to identify people who have been infected with the virus even if they do not have symptoms.
- Testing people before gatherings or events: Rapid antigen tests can help to reduce the risk of spreading the virus at gatherings or events by identifying people who are infected but do not have symptoms.
Limitations of Rapid Antigen Tests
Rapid antigen tests have several limitations, including:
- Lower sensitivity than molecular tests: Rapid antigen tests may not be able to detect the virus in people with low levels of the virus.
- Potential for false positives: Rapid antigen tests can sometimes produce false positive results, which means that the test indicates that a person has COVID-19 when they do not.
- Potential for false negatives: Rapid antigen tests can sometimes produce false negative results, which means that the test indicates that a person does not have COVID-19 when they do.
Conclusion
Rapid antigen tests are a useful tool for diagnosing COVID-19, but they have limitations. It is important to understand the accuracy and limitations of rapid antigen tests before using them to make decisions about your health.